Broadband Tech Examples: Top Choices Explained
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the importance of a robust broadband connection can hardly be overstated. Whether it’s for streaming high-definition videos, engaging in seamless online gaming, or facilitating efficient work-from-home setups, a reliable internet connection stands as the backbone of our digital activities. This article delves into the various types of broadband technologies available, helping you understand which option might be best suited for your needs.
Understanding Broadband Technology
Before we explore the specific types of broadband, it’s essential to grasp what broadband actually is. Broadband refers to high-speed internet access that is always on and faster than traditional dial-up access. The term encompasses several high-speed transmission technologies, each with unique advantages and deployment methods.
Types of Broadband Connections
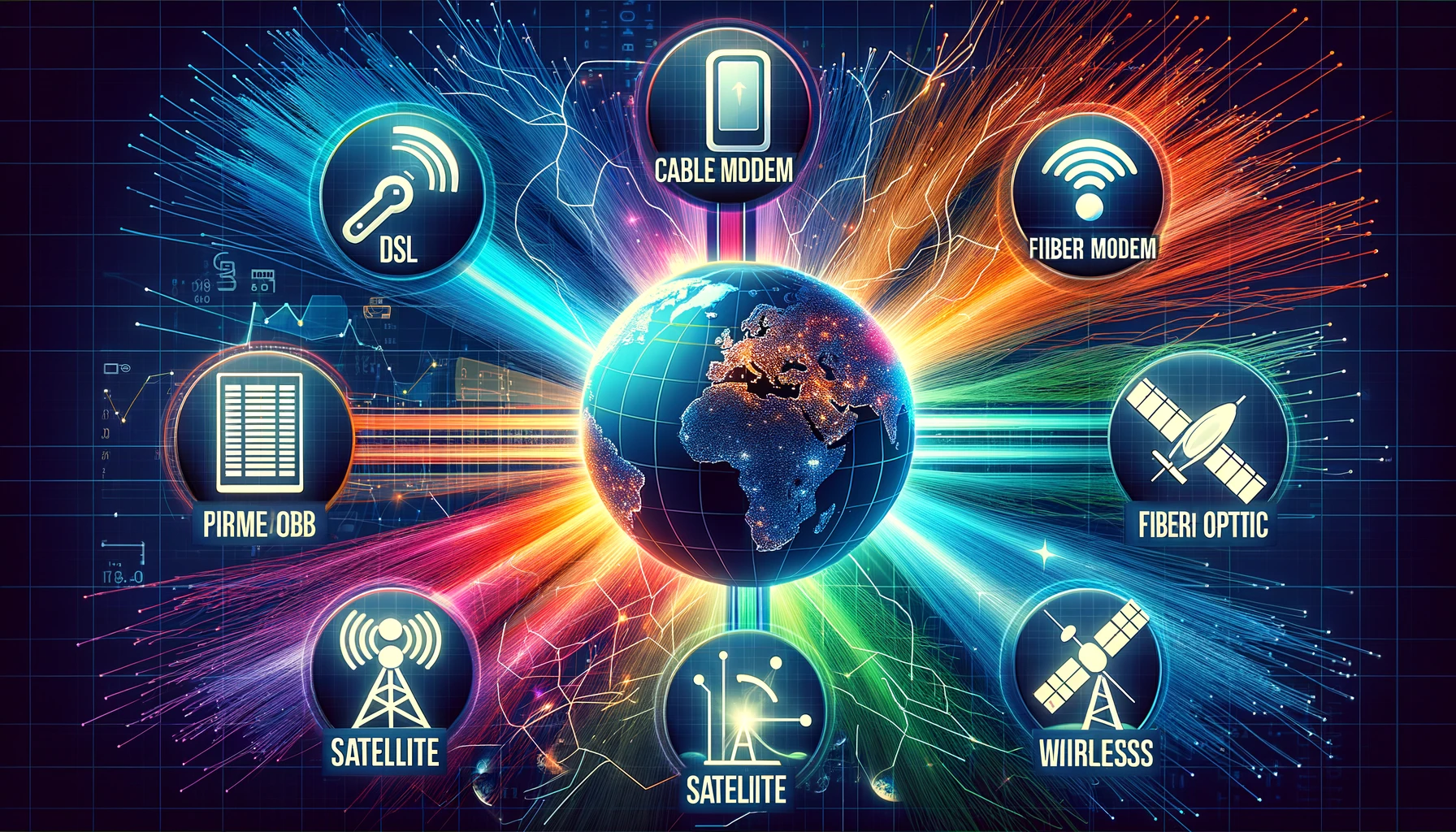
1. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
DSL is one of the oldest forms of broadband technology but remains relevant due to its widespread availability and cost-effectiveness. It operates over regular telephone lines to deliver download speeds in the range of 5 to 35 Mbps. While not the fastest, DSL is a reliable choice for average household usage and small businesses, particularly in rural areas where other forms of broadband may not be available.
2. Cable Modem
Cable broadband utilizes the same lines that deliver cable television services. Typically offering higher speeds than DSL, cable speeds can range from 10 Mbps to over 1 Gbps. One of the main advantages of cable is its speed stability, which is less affected by the distance from the provider’s central location compared to DSL. However, cable connections may suffer from bandwidth congestion during peak usage times, which can slow down speeds.
3. Fiber Optic
When it comes to speed and reliability, fiber optic technology is at the forefront. Unlike DSL and cable, fiber transmits data at the speed of light through strands of glass. The result is significantly faster download and upload speeds that can reach up to 1 Gbps or more. Fiber is particularly suitable for intensive online activities like streaming 4K videos, online gaming, and large file transfers. Despite its benefits, fiber’s availability is limited to urban and some suburban areas.
4. Satellite
For those in remote areas, satellite broadband can be a game-changer. It works by transmitting internet data through a satellite orbiting the Earth. This means it can reach almost anywhere on the planet. The typical speeds for satellite internet range from 10 to 100 Mbps. The downside is that satellite connections can be susceptible to weather disturbances and generally have higher latency, making them less ideal for real-time applications like online gaming.
5. Fixed Wireless
Fixed wireless broadband is delivered through radio signals from a nearby base station to a fixed antenna in your home or business. This type of connection is often faster to set up and can offer speeds comparable to DSL and cable. Fixed wireless is particularly valuable in rural areas that lack the infrastructure for DSL or cable services.
Choosing the Right Broadband Technology
Selecting the right broadband technology depends mainly on your specific needs and location. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Availability: Check what types of broadband are available in your area.
- Speed Requirements: Consider the activities you regularly engage in. Fiber, although more expensive, may be worthwhile for very high-speed needs, whereas DSL might suffice for lighter usage.
- Latency Sensitivity: If you play online games or use real-time applications, low-latency options like cable or fiber are preferable.
- Budget: Determine your budget. DSL and fixed wireless are generally cheaper than fiber and cable.

Conclusion
Understanding the different types of broadband technologies can help you make an informed decision about which internet service to choose. Each technology has its strengths and limitations, and the right choice depends on individual requirements such as speed, budget, and availability. By considering these factors, you can select a broadband service that best fits your digital lifestyle and ensures that you stay connected efficiently and reliably.
In summary, whether you opt for the ubiquitous reach of DSL, the high performance of fiber, or the unique capabilities of satellite or fixed wireless, knowing the nuances of each technology will enable you to maximize your internet experience.